Tags (FREE)
In Git, a tag marks an important point in a repository's history. Git supports two types of tags:
- Lightweight tags point to specific commits, and contain no other information. Also known as soft tags. Create or remove them as needed.
- Annotated tags contain metadata, can be signed for verification purposes, and can't be changed.
The creation or deletion of a tag can be used as a trigger for automation, including:
- Using a webhook to automate actions like Slack notifications.
- Signaling a repository mirror to update.
- Running a CI/CD pipeline with
if: $CI_COMMIT_TAG.
When you create a release, GitLab also creates a tag to mark the release point. Many projects combine an annotated release tag with a stable branch. Consider setting deployment or release tags automatically.
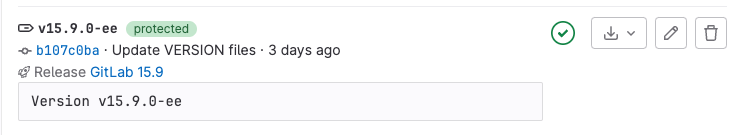
In the GitLab UI, each tag displays:
- The tag name. ({tag})
- Optional. If the tag is protected, a protected badge.
- The commit SHA ({commit}), linked to the commit's contents.
- The commit's title and creation date.
- Optional. A link to the release ({rocket}).
- Optional. If a pipeline has been run, the current pipeline status.
- Download links to the source code and artifacts linked to the tag.
- A Create release ({pencil}) link.
- A link to delete the tag.
View tags for a project
To view all existing tags for a project:
- On the top bar, select Main menu > Projects and find your project.
- On the left sidebar, select Repository > Tags.
View tagged commits in the commits list
Introduced in GitLab 15.10.
-
On the top bar, select Main menu > Projects and find your project.
-
On the left sidebar, select Repository > Commits.
-
Commits with a tag are labeled with a tag icon ({tag}) and the name of the tag. This example shows a commit tagged
v1.26.0:
To view the list of commits in this tag, select the tag name.
Create a tag
Tags can be created from the command line, or the GitLab UI.
From the command line
To create either a lightweight or annotated tag from the command line, and push it upstream:
-
To create a lightweight tag, run the command
git tag TAG_NAME, changingTAG_NAMEto your desired tag name. -
To create an annotated tag, run one of the versions of
git tagfrom the command line:# In this short version, the annotated tag's name is "v1.0", # and the message is "Version 1.0". git tag -a v1.0 -m "Version 1.0" # Use this version to write a longer tag message # for annotated tag "v1.0" in your text editor. git tag -a v1.0 -
Push your tags upstream with
git push origin --tags.
From the UI
To create a tag from the GitLab UI:
- On the top bar, select Main menu > Projects and find your project.
- On the left sidebar, select Repository > Tags.
- Select New tag.
- Provide a Tag name.
- For Create from, select an existing branch name, tag, or commit SHA.
- Optional. Add a Message to create an annotated tag, or leave blank to create a lightweight tag.
- Select Create tag.
Prevent tag deletion (PREMIUM)
To prevent users from removing a tag with git push, create a push rule.
Trigger pipelines from a tag
GitLab CI/CD provides a CI_COMMIT_TAG variable
to identify tags. Use this variable in job rules and workflow rules to test if the pipeline
was triggered by a tag.
In your .gitlab-ci.yml file for the CI/CD pipeline configuration of your project,
you can trigger based on a new tag:
- At the job level, with the
onlykeyword. - At the pipeline level, with the workflow rules keywords.