Check for background migrations before upgrading
Certain releases may require different migrations to be finished before you update to the newer version.
There are two kinds of migrations:
- Background migrations
- Batched background migrations (available in GitLab 14.0 and later)
Background migrations and batched migrations are not the same, so you should check that both are complete before updating.
Decrease the time required to complete these migrations by increasing the number of
Sidekiq workers
that can process jobs in the background_migration queue.
Background migrations
Pending migrations
For Omnibus installations:
sudo gitlab-rails runner -e production 'puts Gitlab::BackgroundMigration.remaining'
sudo gitlab-rails runner -e production 'puts Gitlab::Database::BackgroundMigration::BatchedMigration.queued.count'For installations from source:
cd /home/git/gitlab
sudo -u git -H bundle exec rails runner -e production 'puts Gitlab::BackgroundMigration.remaining'
sudo -u git -H bundle exec rails runner -e production 'puts Gitlab::Database::BackgroundMigration::BatchedMigration.queued.count'Failed migrations
For Omnibus installations:
For GitLab 14.0-14.9:
sudo gitlab-rails runner -e production 'puts Gitlab::Database::BackgroundMigration::BatchedMigration.failed.count'For GitLab 14.10 and later:
sudo gitlab-rails runner -e production 'puts Gitlab::Database::BackgroundMigration::BatchedMigration.with_status(:failed).count'For installations from source:
For GitLab 14.0-14.9:
cd /home/git/gitlab
sudo -u git -H bundle exec rails runner -e production 'puts Gitlab::Database::BackgroundMigration::BatchedMigration.failed.count'For GitLab 14.10 and later:
cd /home/git/gitlab
sudo -u git -H bundle exec rails runner -e production 'puts Gitlab::Database::BackgroundMigration::BatchedMigration.with_status(:failed).count'Batched background migrations (FREE SELF)
- Introduced in GitLab 13.11, behind a feature flag, disabled by default.
- Enabled by default in GitLab 13.12.
- Enabled on GitLab.com.
- Recommended for production use.
- For GitLab self-managed instances, GitLab administrators can opt to disable it.
There can be risks when disabling released features. Refer to this feature's version history for more details.
To update database tables in batches, GitLab can use batched background migrations. These migrations
are created by GitLab developers and run automatically on upgrade. However, such migrations are
limited in scope to help with migrating some integer database columns to bigint. This is needed to
prevent integer overflow for some tables.
Some installations may need to run GitLab 14.0 for at least a day to complete the database changes introduced by that upgrade.
Batched background migrations are handled by Sidekiq and run in isolation, so an instance can remain operational while the migrations are processed. However, there may be performance degradation on larger instances that are heavily used while batched background migrations are run, so it's a good idea to actively monitor the Sidekiq status until all migrations are completed.
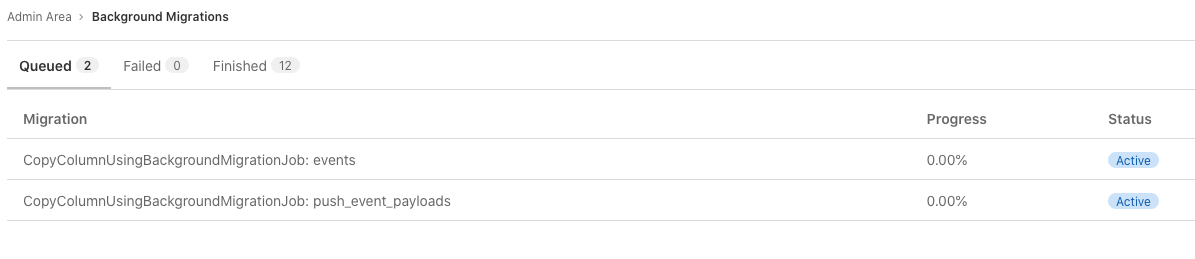
Check the status of batched background migrations
To check the status of batched background migrations:
-
On the top bar, select Main menu > Admin.
-
On the left sidebar, select Monitoring > Background Migrations.
All migrations must have a Finished status before you upgrade GitLab.
The status of batched background migrations can also be queried directly in the database.
-
Log into a
psqlprompt according to the directions for your instance's installation method (for example,sudo gitlab-psqlfor Omnibus installations). -
Run the following query in the
psqlsession to see details on incomplete batched background migrations:select job_class_name, table_name, column_name, job_arguments from batched_background_migrations where status <> 3;
If the migrations are not finished and you try to update to a later version, GitLab prompts you with an error:
Expected batched background migration for the given configuration to be marked as 'finished', but it is 'active':If you get this error, check the batched background migration options to complete the upgrade.
Pause batched background migrations in GitLab 14.x
To pause an ongoing batched background migration, disable the batched background migrations feature. Disabling the feature completes the current batch of migrations, then waits to start the next batch until after the feature is enabled again.
Use the following database queries to see the state of the current batched background migration:
-
Obtain the ID of the running migration:
SELECT id, job_class_name, table_name, column_name, job_arguments FROM batched_background_migrations WHERE status <> 3; -
Run this query, replacing
XXwith the ID you obtained in the previous step, to see the status of the migration:SELECT started_at, finished_at, finished_at - started_at AS duration, min_value, max_value, batch_size, sub_batch_size FROM batched_background_migration_jobs WHERE batched_background_migration_id = XX ORDER BY id DESC limit 10; -
Run the query multiple times within a few minutes to ensure no new row has been added. If no new row has been added, the migration has been paused.
-
After confirming the migration has paused, restart the migration (using the
enablecommand above) to proceed with the batch when ready. On larger instances, background migrations can take as long as 48 hours to complete each batch.
Automatic batch size optimization
- Introduced in GitLab 13.12, behind a feature flag, enabled by default.
- Enabled on GitLab.com.
- Recommended for production use.
- For GitLab self-managed instances, GitLab administrators can opt to disable it.
There can be risks when disabling released features. Refer to this feature's version history for more details.
To maximize throughput of batched background migrations (in terms of the number of tuples updated per time unit), batch sizes are automatically adjusted based on how long the previous batches took to complete.
Enable or disable automatic batch size optimization
Automatic batch size optimization for batched background migrations is under development but ready for production use. It is deployed behind a feature flag that is enabled by default. GitLab administrators with access to the GitLab Rails console can opt to disable it.
To enable it:
Feature.enable(:optimize_batched_migrations)To disable it:
Feature.disable(:optimize_batched_migrations)Parallel execution
- Introduced in GitLab 15.7, behind a feature flag, enabled by default.
- Enabled on GitLab.com.
- Recommended for production use.
- For GitLab self-managed instances, GitLab administrators can opt to disable it.
There can be risks when disabling released features. Refer to this feature's version history for more details.
To speed up the execution of batched background migrations, two migrations are executed at the same time.
GitLab administrators with access to the GitLab Rails console can change the number of batched background migrations executed in parallel:
ApplicationSetting.update_all(database_max_running_batched_background_migrations: 4)Enable or disable parallel execution for batched background migrations
Parallel execution for batched background migrations is under development but ready for production use. It is deployed behind a feature flag that is enabled by default. GitLab administrators with access to the GitLab Rails console can opt to disable it.
To enable it:
Feature.enable(:batched_migrations_parallel_execution)To disable it:
Feature.disable(:batched_migrations_parallel_execution)Troubleshooting
Enable or disable background migrations
In extremely limited circumstances, a GitLab administrator can disable either or both of these feature flags:
execute_background_migrationsexecute_batched_migrations_on_schedule
These flags are enabled by default. Disable them only as a last resort to limit database operations in special circumstances, like database host maintenance.
WARNING:
Do not disable either of these flags unless you fully understand the ramifications. If you disable
the execute_background_migrations or execute_batched_migrations_on_schedule feature flag,
GitLab upgrades might fail and data loss might occur.
Database migrations failing because of batched background migration not finished
When updating to GitLab 14.2 or later there might be a database migration failing with a message like:
StandardError: An error has occurred, all later migrations canceled:
Expected batched background migration for the given configuration to be marked as 'finished', but it is 'active':
{:job_class_name=>"CopyColumnUsingBackgroundMigrationJob", :table_name=>"push_event_payloads", :column_name=>"event_id", :job_arguments=>[["event_id"], ["event_id_convert_to_bigint"]]}First, check if you have followed the version-specific upgrade instructions for 14.2. If you have, you can manually finish the batched background migration. If you haven't, choose one of the following methods:
- Rollback and upgrade through one of the required versions before updating to 14.2+.
- Roll forward, staying on the current version and manually ensuring that the batched migrations complete successfully.
Roll back and follow the required upgrade path
- Rollback and restore the previously installed version
- Update to either 14.0.5 or 14.1 before updating to 14.2+
- Check the status of the batched background migrations and make sure they are all marked as finished before attempting to upgrade again. If any remain marked as active, you can manually finish them.
Roll forward and finish the migrations on the upgraded version
For a deployment with downtime
To run all the batched background migrations, it can take a significant amount of time depending on the size of your GitLab installation.
-
Check the status of the batched background migrations in the database, and manually run them with the appropriate arguments until the status query returns no rows.
-
When the status of all of all them is marked as complete, re-run migrations for your installation.
-
Complete the database migrations from your GitLab upgrade:
sudo gitlab-rake db:migrate -
Run a reconfigure:
sudo gitlab-ctl reconfigure -
Finish the upgrade for your installation.
For a no-downtime deployment
As the failing migrations are post-deployment migrations, you can remain on a running instance of the upgraded version and wait for the batched background migrations to finish.
- Check the status of the batched background migration from the error message, and make sure it is listed as finished. If it is still active, either wait until it is done, or manually finish it.
- Re-run migrations for your installation, so the remaining post-deployment migrations finish.
Manually finishing a batched background migration
Introduced in GitLab 14.1
If you need to manually finish a batched background migration due to an error, you can run:
sudo gitlab-rake gitlab:background_migrations:finalize[<job_class_name>,<table_name>,<column_name>,'<job_arguments>']Replace the values in angle brackets with the correct arguments. For example, if you receive an error similar to this:
StandardError: An error has occurred, all later migrations canceled:
Expected batched background migration for the given configuration to be marked as 'finished', but it is 'active':
{:job_class_name=>"CopyColumnUsingBackgroundMigrationJob", :table_name=>"push_event_payloads", :column_name=>"event_id", :job_arguments=>[["event_id"], ["event_id_convert_to_bigint"]]}Plug the arguments from the error message into the command:
sudo gitlab-rake gitlab:background_migrations:finalize[CopyColumnUsingBackgroundMigrationJob,push_event_payloads,event_id,'[["event_id"]\, ["event_id_convert_to_bigint"]]']If you need to manually run a batched background migration to continue an upgrade, you can check the status in the database and get the arguments from the query results. For example, if the query returns this:
job_class_name | table_name | column_name | job_arguments
---------------------------------------+------------+-------------+------------------------------------
CopyColumnUsingBackgroundMigrationJob | events | id | [["id"], ["id_convert_to_bigint"]]The results from the query can be plugged into the command:
sudo gitlab-rake gitlab:background_migrations:finalize[CopyColumnUsingBackgroundMigrationJob,events,id,'[["id"]\, ["id_convert_to_bigint"]]']Mark a batched migration finished
There can be cases where the background migration fails: when jumping too many version upgrades, or backward-incompatible database schema changes. (For an example, see issue 393216). Failed background migrations prevent further application upgrades.
When the background migration is determined to be "safe" to skip, the migration can be manually marked finished:
WARNING: Make sure you create a backup before proceeding.
# Start the rails console
connection = ApplicationRecord.connection # or Ci::ApplicationRecord.connection, depending on which DB was the migration scheduled
Gitlab::Database::SharedModel.using_connection(connection) do
migration = Gitlab::Database::BackgroundMigration::BatchedMigration.find_for_configuration(
Gitlab::Database.gitlab_schemas_for_connection(connection),
'BackfillUserDetailsFields',
:users,
:id,
[]
)
# mark all jobs completed
migration.batched_jobs.update_all(status: Gitlab::Database::BackgroundMigration::BatchedJob.state_machine.states['succeeded'].value)
migration.update_attribute(:status, Gitlab::Database::BackgroundMigration::BatchedMigration.state_machine.states[:finished].value)
end
The BackfillNamespaceIdForNamespaceRoute batched migration job fails
In GitLab 14.8, the BackfillNamespaceIdForNamespaceRoute batched background migration job
may fail to complete. When retried, a 500 Server Error is returned. This issue was
resolved in GitLab 14.9.
To resolve this issue, upgrade GitLab from 14.8 to 14.9. You can ignore the failed batch migration until after you update to GitLab 14.9.
Background migrations remain in the Sidekiq queue
WARNING: The following operations can disrupt your GitLab performance. They run a number of Sidekiq jobs that perform various database or file updates.
Run the following check. If it returns non-zero and the count does not decrease over time, follow the rest of the steps in this section.
# For Omnibus installations:
sudo gitlab-rails runner -e production 'puts Gitlab::BackgroundMigration.remaining'
# For installations from source:
cd /home/git/gitlab
sudo -u git -H bundle exec rails runner -e production 'puts Gitlab::BackgroundMigration.remaining'It is safe to re-execute the following commands, especially if you have 1000+ pending jobs which would likely overflow your runtime memory.
For Omnibus installations
# Start the rails console
sudo gitlab-rails c
# Execute the following in the rails console
scheduled_queue = Sidekiq::ScheduledSet.new
pending_job_classes = scheduled_queue.select { |job| job["class"] == "BackgroundMigrationWorker" }.map { |job| job["args"].first }.uniq
pending_job_classes.each { |job_class| Gitlab::BackgroundMigration.steal(job_class) }For installations from source
# Start the rails console
sudo -u git -H bundle exec rails RAILS_ENV=production
# Execute the following in the rails console
scheduled_queue = Sidekiq::ScheduledSet.new
pending_job_classes = scheduled_queue.select { |job| job["class"] == "BackgroundMigrationWorker" }.map { |job| job["args"].first }.uniq
pending_job_classes.each { |job_class| Gitlab::BackgroundMigration.steal(job_class) }Background migrations stuck in 'pending' state
WARNING: The following operations can disrupt your GitLab performance. They run a number of Sidekiq jobs that perform various database or file updates.
- GitLab 13.6 introduced an issue where a background migration named
BackfillJiraTrackerDeploymentType2can be permanently stuck in a pending state across upgrades. To clean up this stuck migration, see the 13.6.0 version-specific instructions. - GitLab 14.2 introduced an issue where a background migration named
BackfillDraftStatusOnMergeRequestscan be permanently stuck in a pending state across upgrades when the instance lacks records that match the migration's target. To clean up this stuck migration, see the 14.2.0 version-specific instructions. - GitLab 14.4 introduced an issue where a background migration named
PopulateTopicsTotalProjectsCountCachecan be permanently stuck in a pending state across upgrades when the instance lacks records that match the migration's target. To clean up this stuck migration, see the 14.4.0 version-specific instructions. - GitLab 14.5 introduced an issue where a background migration named
UpdateVulnerabilityOccurrencesLocationcan be permanently stuck in a pending state across upgrades when the instance lacks records that match the migration's target. To clean up this stuck migration, see the 14.5.0 version-specific instructions. - GitLab 14.8 introduced an issue where a background migration named
PopulateTopicsNonPrivateProjectsCountcan be permanently stuck in a pending state across upgrades. To clean up this stuck migration, see the 14.8.0 version-specific instructions. - GitLab 14.9 introduced an issue where a background migration named
ResetDuplicateCiRunnersTokenValuesOnProjectscan be permanently stuck in a pending state across upgrades when the instance lacks records that match the migration's target. To clean up this stuck migration, see the 14.9.0 version-specific instructions.
For other background migrations stuck in pending, run the following check. If it returns non-zero and the count does not decrease over time, follow the rest of the steps in this section.
# For Omnibus installations:
sudo gitlab-rails runner -e production 'puts Gitlab::Database::BackgroundMigrationJob.pending.count'
# For installations from source:
cd /home/git/gitlab
sudo -u git -H bundle exec rails runner -e production 'puts Gitlab::Database::BackgroundMigrationJob.pending.count'It is safe to re-attempt these migrations to clear them out from a pending status:
For Omnibus installations
# Start the rails console
sudo gitlab-rails c
# Execute the following in the rails console
Gitlab::Database::BackgroundMigrationJob.pending.find_each do |job|
puts "Running pending job '#{job.class_name}' with arguments #{job.arguments}"
result = Gitlab::BackgroundMigration.perform(job.class_name, job.arguments)
puts "Result: #{result}"
endFor installations from source
# Start the rails console
sudo -u git -H bundle exec rails RAILS_ENV=production
# Execute the following in the rails console
Gitlab::Database::BackgroundMigrationJob.pending.find_each do |job|
puts "Running pending job '#{job.class_name}' with arguments #{job.arguments}"
result = Gitlab::BackgroundMigration.perform(job.class_name, job.arguments)
puts "Result: #{result}"
end